Semaphore v2.16 makes built-in Swagger API documentation available in the open source version, introduces task parameters for Schedules and Integrations, and adds support for SQLite.
Тable of contents
-
Features
-
Built-in Swagger API Documentation
Access comprehensive API documentation directly within Semaphore’s interface, enabling seamless integration with external tools and CI/CD pipelines.
Learn more » -
Tasks parameters for Schedules and Integrations
Define and pass custom parameters to tasks triggered by Schedules and Integrations, enabling more flexible and dynamic automation workflows.
Learn more » -
SQLite support
Seamlessly run Semaphore with a lightweight, file-based database engine for easier setup and local development.
Learn more » -
BoltDB has been deprecated
BoltDB is now deprecated in favor of SQLite, providing a more robust and maintainable database option.
Learn more » -
Parallel tasks for the same Template
You can now run multiple concurrent tasks from the same Template, enabling greater throughput and flexibility in your automation workflows.
Learn more » -
HashiCorp Vault support (PRO)
Learn more »
-
Features
Built-in Swagger API Documentation (PRO)
Semaphore users can now access comprehensive API documentation through an integrated Swagger UI interface. This powerful feature enables DevOps teams to:
- Browse and explore all available API endpoints
- View detailed parameter specifications and response formats
- Execute test requests directly from the interface
- Streamline integration with external tools and CI/CD pipelines
- Accelerate development of custom automation solutions
The built-in Swagger documentation makes it easier than ever to integrate Semaphore with your existing DevOps toolchain and custom automation workflows.

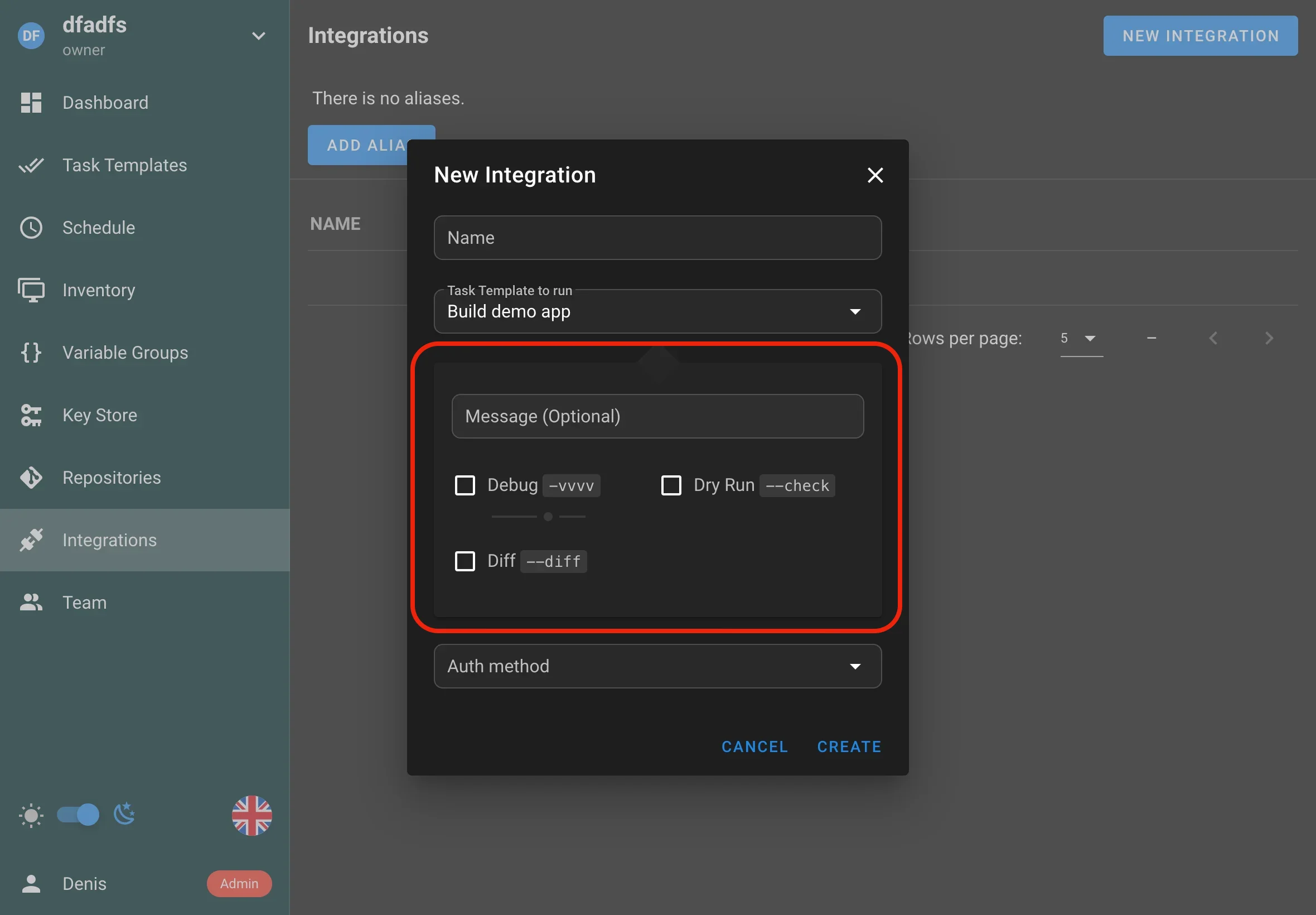
Tasks parameters for Schedules and Integrations
Semaphore now allows you to define and pass parameters to tasks that are executed via Schedules and Integrations. This enhancement brings the full power of task parameters to every automation entry point in Semaphore, enabling you to:
- Inject variables such as environment names, Git branches, or feature flags directly into your Ansible playbooks and Terraform plans.
- Reuse the same templates across multiple scenarios without duplicating code.
- Build dynamic, context-aware workflows that adapt to how they are triggered.
SQLite support
Semaphore now supports using SQLite as its database engine. This lightweight, file-based option makes it dramatically easier to get Semaphore up and running in environments where managing an external PostgreSQL instance is overkill.
Key advantages include:
- Zero external dependencies – everything is stored in a single
.sqlitefile that lives alongside the application. - Ideal for local development and small teams – spin up a full Semaphore instance on a laptop or inside CI without additional services.
- Fast setup in containerized and edge environments – perfect for demos, PoC deployments, and ephemeral test environments.
- Seamless migration path – start with SQLite and move to PostgreSQL later using the built-in export/import commands.
BoltDB has been deprecated
BoltDB served as the embedded key-value store for Semaphore since its earliest versions. As of v2.16 it is officially deprecated and will be removed in a future major release.
Why the change?
- Single-writer limitation – BoltDB allows only one concurrent writer, which limits scalability on busy installations.
- Migration friction – evolving data structures requires bespoke application code.
SQLite now replaces BoltDB as the default storage engine (see the SQLite support section).
Impact on existing users
- Current BoltDB installations continue to run, but no new features will be tested against Bolt.
- New installations default to SQLite and can no longer create fresh BoltDB databases.
- Official support for BoltDB will be discontinued ~6 months after this release.
- Migration script will be available soon.
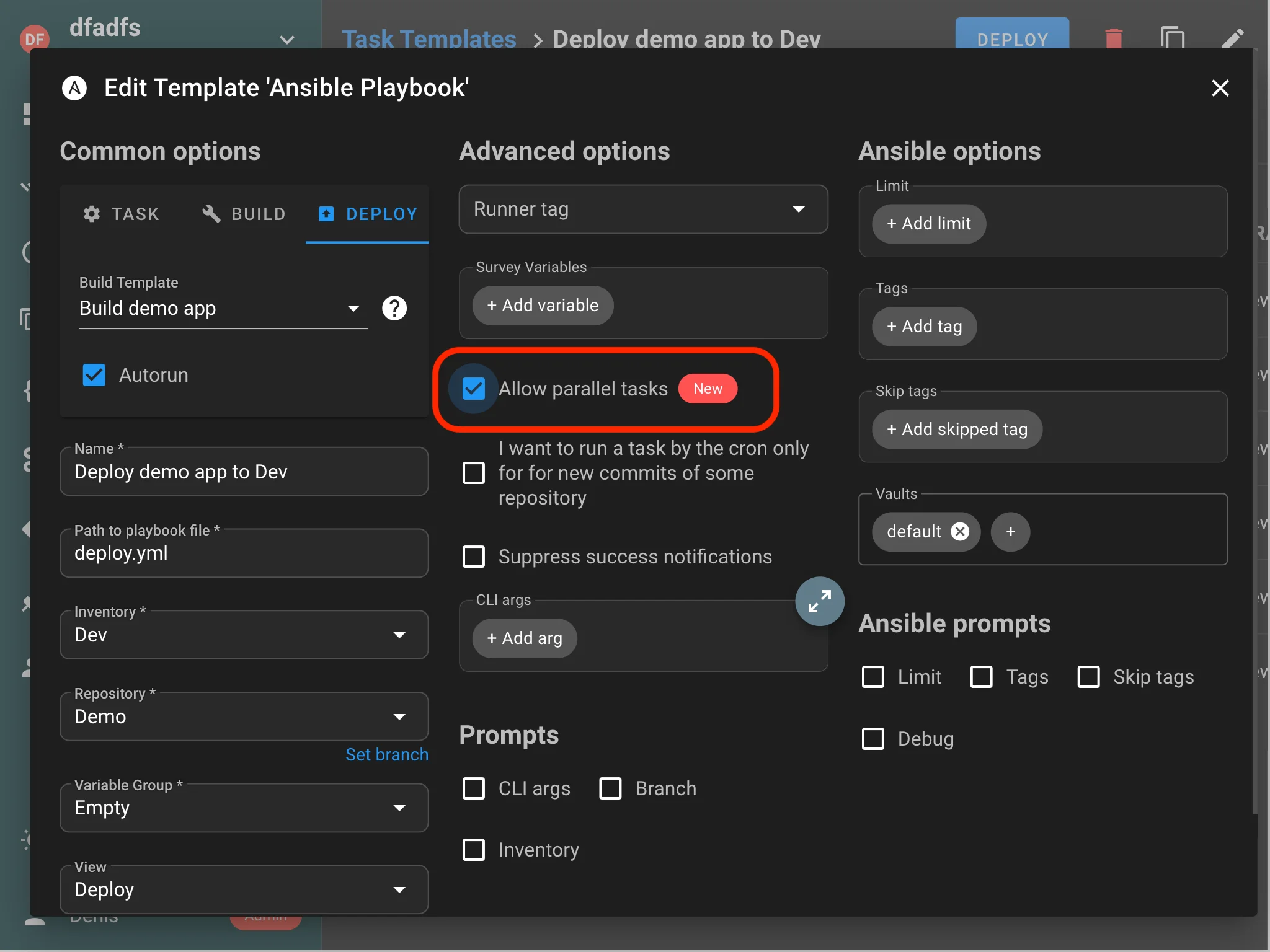
Parallel tasks for the same Template
Semaphore now allows you to run multiple concurrent tasks from the same template, significantly improving throughput for high-demand automation workflows. By default, tasks from the same template are queued sequentially to prevent resource conflicts and ensure predictable execution order.
How it works:
- Sequential execution (default): Tasks from the same template are queued and executed one after another, preventing resource conflicts and maintaining predictable execution order.
- Parallel execution: Enable the “Allow parallel tasks” checkbox in template settings to run multiple instances of the same template simultaneously.
This feature is particularly useful for scenarios like rolling deployments, parallel environment updates, or when multiple developers need to run the same automation workflow simultaneously.
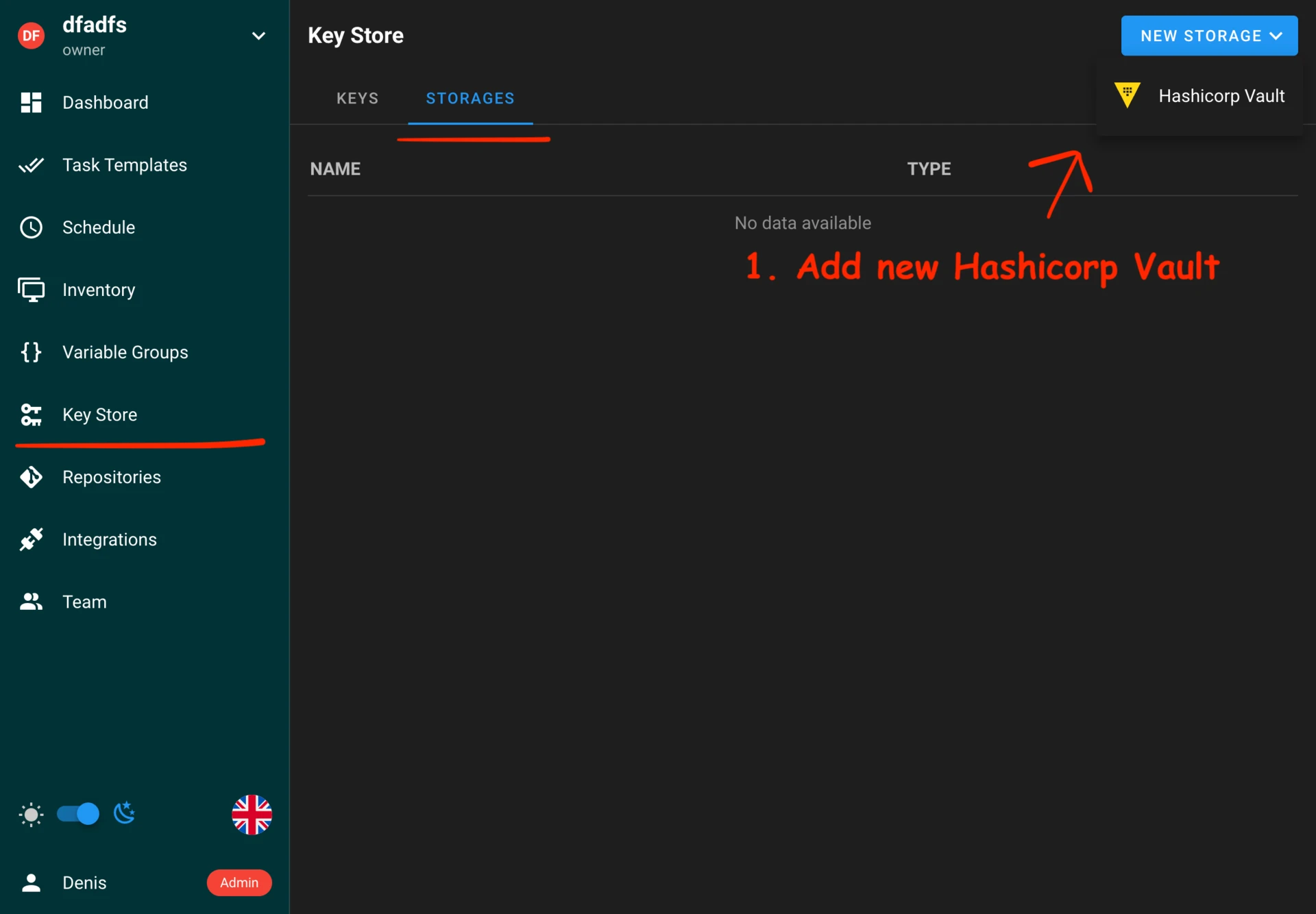
HashiCorp Vault support (PRO)
Semaphore now offers native integration with HashiCorp Vault for secure key management. When creating or updating a secret in the Semaphore UI, you can choose whether to store it in the built-in database or in your the Vault instance. This gives you the flexibility to manage sensitive credentials according to your security requirements and existing infrastructure.
Key benefits:
- Flexible storage: Select on a per-secret basis whether to store credentials in the Semaphore database or in Vault.
- Improved security: Secrets stored in Vault never reside in the Semaphore database and are accessed only when needed.
- Centralized management: Use Vault’s tooling to manage, rotate, and audit secrets stored externally.
- Seamless integration: Easily connect Semaphore to your existing Vault deployment with minimal configuration.
- Access control: Leverage Vault’s fine-grained policies to control which users and projects can access specific secrets.
This feature is available in Semaphore PRO and is ideal for organizations with strict security requirements or those already using Vault for secret management.